AI Chatbot Project Implementation: A Step-by-Step Guide for Managers
Table of contents
- Stage 1: Identifying Customer Needs
- Stage 2: Process Analysis
- Stage 3: Chatbot Implementation on the Platform and Tests
- Stage 4: Pilot Production Deployment
- Stage 5: Chatbot Maintenance and Development
- Work with SentiOne – Your Bot-Building Partner
- Article Summary
So, you’ve chosen a technological partner that will help you build your chatbot or voice bot – now what? There are five essential stages of any bot-building project, and you should know and follow them in order to ensure smooth cooperation with your partner and the delivery of a successful bot that your customers want to talk to. And that’s what we want to discuss in this post.
The main stages of a bot-building project that we will discuss in this article are as follows:
- Identifying customer needs
- Process analysis
- Chatbot implementation and testing
- Pilot production deployment
- Chatbot maintenance and development
Following this process ensures you get a virtual assistant that’s not only correctly designed from a technical standpoint but also helpful when it comes to supporting your team with repetitive everyday tasks.
Without further ado, let’s get down to the details.
Stage 1: Identifying Customer Needs
Your future chatbot has to address a certain use case and bring tangible results – it should support your customers in dealing with everyday tasks such as booking an appointment, asking for order status, and more. This stage is essential as it shapes the whole chatbot design process. That’s why everyone involved in direct work with customers should be included.
Stakeholders
Identifying customer needs should happen with the participation of:
- A project sponsor (typically, that’s management or a manager/director who’s responsible for customer service)
- A project manager (a person responsible for the oversight of the entire design process; in smaller organisations, a project sponsor and a project manager can be the same person)
- An analysts (their job is to provide your company with the necessary data and trends concerning customer service, e.g., what are the typical problems customers have)
- A Contact centre team (naturally, you don’t have to include all the consultants you have on your team; captains and supervisors usually are sufficient)
What you need to do
Your bot provider will most likely schedule a chatbot workshop. This part is important, especially when that’s the first AI chatbot project for your company. You want to make sure that everyone involved in the chatbot design process understands conversational AI basics, NLU basics, all the specific terms, and how a chatbot can be made using an online platform.
The next thing to do is a design thinking workshop. During such a workshop, your team should discuss the chatbot’s goals (what it should do), identify the target audience (who it should serve), KPIs (how to know your chatbot is useful), and a chatbot persona (how your chatbot should look and behave).
At this point, it’s worth discussing a chatbot prototype – what features it should have so that your company can assess the profitability of the project without investing too much money.
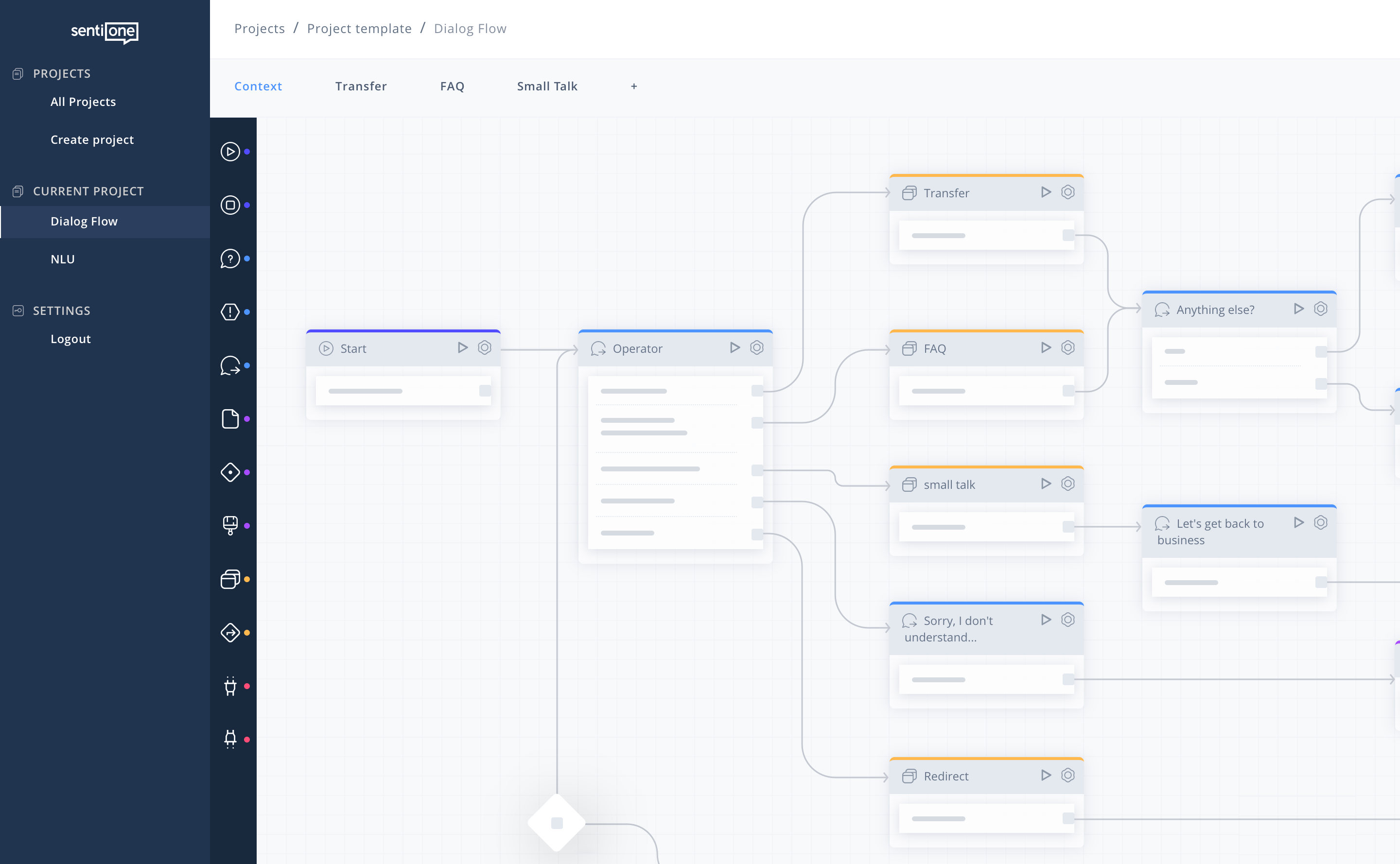
SentiOne Automate: Chatbot dialog flow
Stage results
As a result of this analysis and workshops, you should end up with a clear document describing the scope of this AI chatbot project, along with all the important elements that need to be addressed during the chatbot development process. It doesn’t have to be anything complicated; a simple Word document will do.
Stage 2: Process Analysis
Now, it’s time to dig deeper and get the full picture of how your future bot should work and behave. Above all, your company (together with the bot provider) must assess which part of the e.g., customer service process should be automated. This requires having a closer look at your processes.
Stakeholders
This time, your team can be a bit smaller. During this strictly operational part of the work, you need to include your project manager, at least one business analyst, and your call centre team.
What you need to do
For starters, it’s essential to understand how customers communicate with your company. What channels are they using? What are they asking for? What answer are they getting? What data sources are necessary in the process (for instance, e-commerce chatbots need access to your e-commerce platform, inventory levels, as well as order lists).
When your team decides there is potential to automate some of the customer interactions, you can start working on the chatbot’s design. First off, you need to concentrate on two important aspects:
Modelling of business processes for automation
The work starts with the preparation of diagrams presenting current customer-related business processes. Again, let’s use an example: If you run an online store, you need to outline the whole purchasing process, from the first visit to your website up to the checkout and payment for the order. To some extent, you need to create a customer journey map. Once it’s done, you can identify areas with automation potential. For instance, if customers frequently ask about order status, you can use your chatbot to automate answering this question.
Modelling of the bot process based on business processes
Having all the business processes outlined, you can start working on bot processes, including bot responses and communication triggers. This is when you also work on a set of phrases (customer utterances) and define the chatbot’s intents. It is also vital to think about future integration possibilities, so that:
- Your bot has access to all the necessary knowledge
- You can use your bot in different communication channels, not just your website
At SentiOne, we make it easy for our clients to integrate their bots with a number of tools and platforms, including WhatsApp, Messenger, X (Twitter), Skype for Business and more.
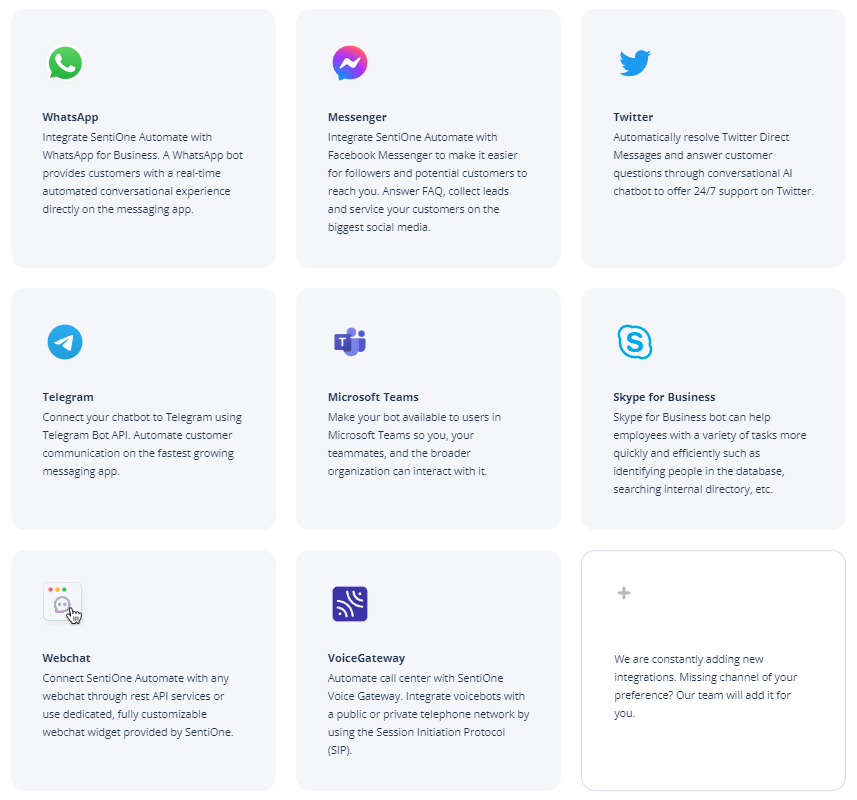
SentiOne Automate: Available chatbot integrations
Results
At the end of this stage, you should have a ready-made list of processes, including:
- Process diagrams
- An initial set of the bot’s phrases and intents
- Future integrations with other tools in your company
Stage 3: Chatbot Implementation on the Platform and Tests
Of course, this stage will look different depending on the provider you’re working with. If you decide to work with SentiOne Automate, you’ll get access to a transparent and intuitive bot-building platform that streamlines the whole process and enables you to modify your bot without extensive coding knowledge.
Stakeholders
In this stage, you should involve your project manager, at least one business analyst, your call centre team, as well as a QA tester.
What you need to do
Put shortly, you need to put all the assumptions and discussed elements to work, and start working on the bot deployment process. With our low-code/no-code bot- building platform, it’s really easy and doesn’t require advanced IT knowledge.
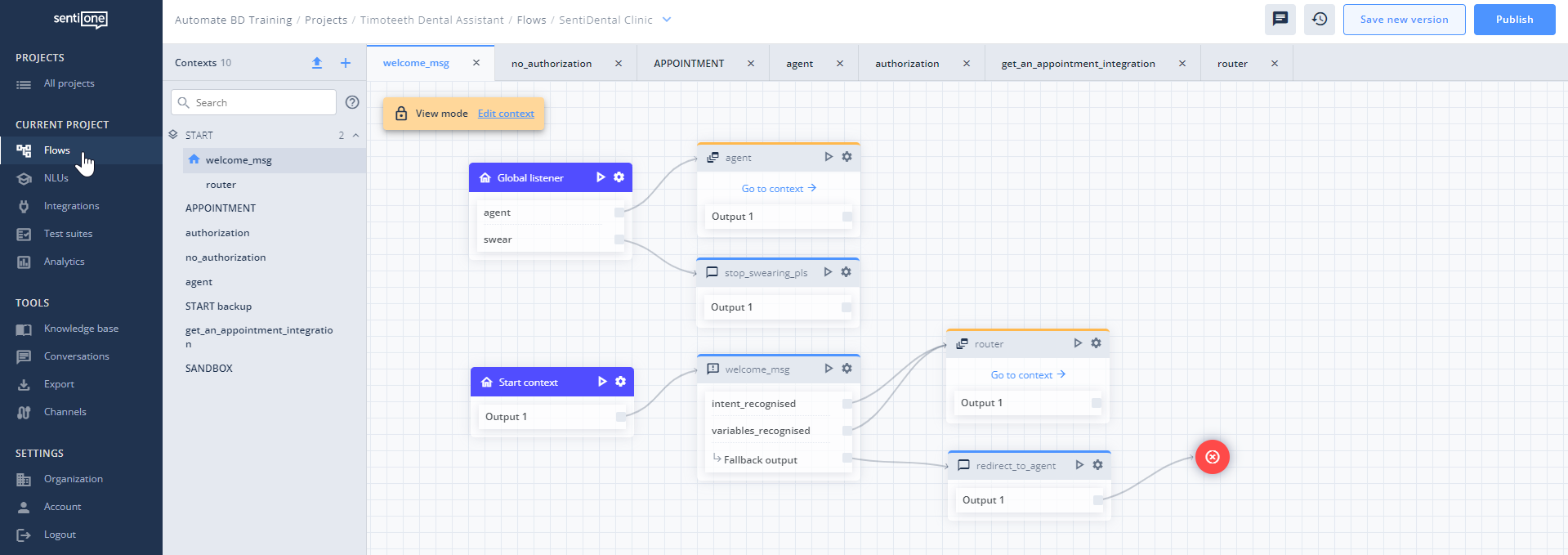
Working on a brand-new bot: Dialog flow development
Use your set of phrases to train your NLU engine (as well as ASR, which stands for Automatic Speech Recognition, when working on a voice bot). NLU testing involves:
- Expansion of the phrase list (during your tests, you may decide that your bot needs to say more or give more definite answers)
- Improvement of intent recognition (is the answer always relevant to the query?)
- Optimisation of individual NLU models (if you’re working on an advanced chatbot working with many different types of interactions)
Once that’s done, you can run some initial tests to spot potential errors and issues. At this point, testing should include:
- Preparation of test scenarios (what do you want to test and how?)
- Running multiple tests among different groups of users (we encourage you to include both employees and people outside of your company to get more reliable feedback)
- Analysis of deployed processes
Of course, when you find out there are some bugs or errors during the process, you need to have a bug-fixing procedure in place.
Naturally, if you’re working on a voice bot instead of a chatbot, you should adjust all these elements to a voice-based assistant.
Now, when all of that is done, you should focus on the last two elements:
- Integrations with other tools in your company (e.g., your CRM system or other platform)
- Performance testing (run some tests to verify the bot’s performance, such as the number of successful concurrent connections)
We know that this stage can seem like a lot, especially for a company creating a chatbot or a voice bot for the first time. However, if you’re working on a relatively straightforward bot, the deployment process doesn’t have to be complicated at all! We invite you to read this article on our blog: How I Built My First Chatbot with SentiOne Automate. You will see how all the things we mentioned in this stage look in practice.
And always remember that our team is here to help you. If you need support with a chatbot or a voice bot deployment, we are happy to assist you.
Results
If this stage was successful, you should have a deployed and tested bot process that is integrated with the necessary tools. You should also have adjusted AI models.
Stage 4: Pilot Production Deployment
In this second to last stage, we focus on solution deployment and monitoring, as well as qualitative analysis of conversations. You need to ensure that the solutions you’ve developed are successfully implemented.
Stakeholders
At this point, your “bot team” should comprise the same people as in the previous step: A project manager, a business analyst, a representative from the contact centre team, and a QA tester.
What you need to do
When it comes to solution deployment and monitoring, make sure that the solutions you’ve developed are now successfully implemented and running smoothly. It’s vital to monitor your bot’s performance to ensure it meets the desired goals. This includes keeping an eye on any potential issues or errors that may arise and taking appropriate actions to address them.
Qualitative analysis of conversation
The next element that needs your attention is the qualitative analysis of conversations. Dive deep into the conversations that take place between users and your system. Carefully analyse the transcriptions and recordings (in the case of a voice bot) of these conversations to gain valuable insights. At this point, your goal is to identify any anomalies or issues in the conversations, such as misunderstandings or problems with recognition. By understanding these issues, you can make improvements to enhance the user experience and ensure hassle-free customer interactions.
Measuring and optimising performance
Additionally, you need to focus on measuring and optimising the performance of your natural language understanding system. Analyse your Recall and Precision metrics (they measure the bot’s ability to correctly identify and retrieve relevant information from its knowledge base as well as the level of precision in the answers it provides), as well as the F1 score (it’s a metric that combines both precision and recall metrics to provide an overall assessment of the bot’s performance) to assess the effectiveness of your NLU capabilities. This helps you identify areas that need improvement and allows you to optimise your NLU system for better accuracy and understanding.
Bot optimisation
Finally, you should concentrate on bot optimisation. Implement necessary changes and updates to optimise the performance of your chatbot. By making continuous improvements, your goal is to enhance the bot’s ability to provide accurate and helpful responses. This involves refining its algorithms and training models and incorporating user feedback to ensure the bot delivers top-notch UX.
Results
At the end of this stage, you should have a fully operational chatbot that’s optimised and aligned with your business requirements and KPIs.
Stage 5: Chatbot Maintenance and Development
Like your company, a chatbot is a “living thing,” and its development should never be stopped. From time to time, you’ll need to check whether everything works as it should; plus, as your company grows, there may be a need to add more conversation scenarios and features to your virtual assistant.
Stakeholders
Just like in step 4, a project manager, a business analyst, a representative of the contact centre team, as well as a QA tester should be involved in the ongoing development of your bot.
What you need to do
Apart from the elements we mentioned in the introduction to this stage, you should focus on the expansion of customer support volume through a chatbot or a voice bot (so that it can serve more and more customers – or perhaps your internal teams too – at the same time) and its production deployment and monitoring. Keep in mind, though, that stage 5 never really ends.
Results
The result of this stage is identical to the outcome of your whole conversational AI chatbot project. You should have a fully operational and deployed bot that constitutes a valuable addition to your company and helps you achieve its business objectives.
Work with SentiOne – Your Bot-Building Partner
At SentiOne Automate, we’re continually working on expanding the capabilities of our low-code/no-code bot-building platform which has already helped many companies devise and deploy their own chatbots.
If you think your company could use a chatbot or a voice bot, you’re probably right! And it’s our role to help you with this conversational AI project. Start today by scheduling a free demo of our platform.
Article Summary
This article presents a step-by-step guide for managers on implementing AI chatbot projects. The process includes identifying customer needs, analysing processes, deploying and testing the chatbot, piloting production, and maintaining the bot.